What are the mystery 'alien' balls found on the ocean floor?
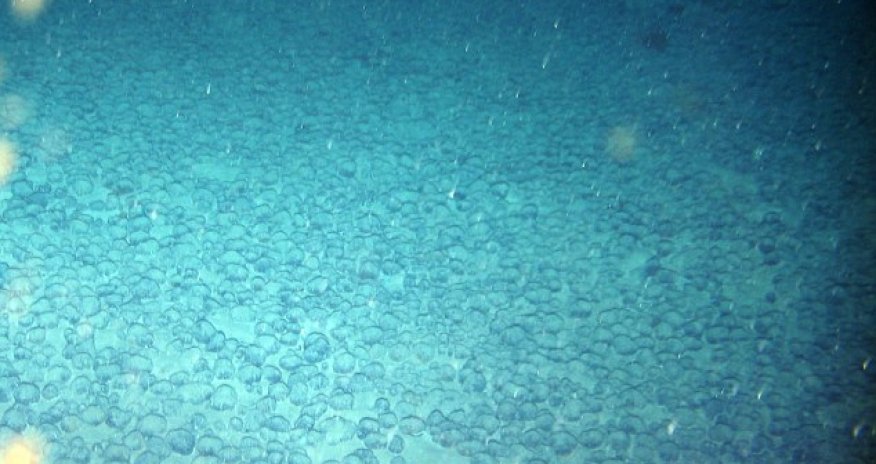

Ever since they were discovered in 1873, scientists have been trying to find out the origin of the millions of potato-sized metal balls that carpet the world's oceans.
Known as manganese nodules, these lumps contain valuable metals that scientists someday hope to harvest from the sea floor.
Now German scientists could be closer to solving the mystery of their origin after stumbling on the largest patch of manganese nodules ever found in the Atlantic.
The R/V Sonne, a research ship, was several hundred miles east of Barbados when a net meant to capture marine life instead captured manganese ore nodules.
A remote camera later revealed that the seafloor was littered with these metal rocks ranging in size from golf balls to bowling balls.
With growth rates of between one to five millimetres in a million years, some of the nodules could be 10 million years old, the researchers said.
'I was surprised, because this is generally not the place you think of for manganese nodules,' said Colin Devey, chief scientist for the expedition at the Geomar Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research told LiveScience.
These particular nodules were discovered in waters roughly 16,400ft and 18,000ft (5,000 and 5,500 metres) deep.
One theory as to how they formed is through chemical reactions in seawater that were boosted by microbes.
Another suggests the nodules were created by precipitation of metals from seawater, especially from volcanic thermal vents.
These metal balls consist of the manganese and contain iron and other coveted metals such as copper, cobalt or zinc.
Since the 1970s, they have been considered a possible source of raw materials.
But due to the large water depths and the associated technical complexity and potential environmental damages, no commercial exploitation is currently in sight.
At the same time, manganese nodules are scientifically of great interest since they can be used as climate and environmental archives.
Manganese nodules grow like a pearl shell around a nucleus and as a result record information on the prevailing environmental conditions.
Since the nodules grow very slowly, they provide a record of the world's early climate history.
Scientists are now hoping to analyse the nodules in greater detail to understand exactly how they formed.
They say greater analysis could also unlock the secrets to our planet's changing climate.
(dailymail.co.uk)
ANN.Az
Similar news
Similar news



































 Photo
Photo 



 Video
Video