Will camel discovery break the Bible's back?
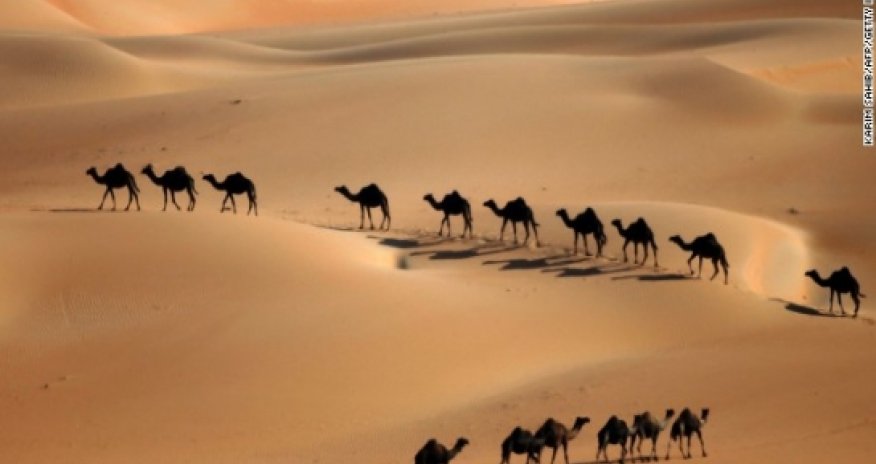

First a Noah’s Ark discovery raised a flood of questions, then there was the much-hyped debate over life’s origins between Bill Nye the Science Guy and creationist Ken Ham.And now this: a scientific report establishing that camels, the basic mode of transportation for the biblical patriarchs, weren’t domesticated in Israel until hundreds of years after Abraham, Isaac and Jacob are said to have wandered the earth.Using radiocarbon dating of camel bones that showed signs of having carried heavy loads, Israeli archaeologists have dated the earliest domesticated camels to the end of the 10th century BCE.But according to the traditional biblical chronology, the patriarchs were schlepping around Canaan on camels over a millennium earlier, all the way back in 2100 BCETaken on its own, this may seem a rather minor problem.After all, this is Genesis, in which some people live to be 900 years old (hello, Methuselah), all of humanity emerges from Babylon, and the Dead Sea is created from the backward glance of Lot’s wife. (Not to mention the six-day creation story and the stuffing of all land animals on a single boat.)How important could camels really be?For those who believe the Bible to be fundamentally true, this is hardly going to change any minds. For those who believe it to be entirely false, this is surely not the most damning piece of evidence.What the camels in Genesis reveal, in fact, has nothing to do with the “truth” of the biblical story at all.Instead, the presence of these camels in the story highlights, in a very clear way, the essential humanity of the biblical writers: like the best authors, they simply wrote about what they knew.The patriarchs are depicted as nomadic, never settling for long in one place, but moving constantly from location to location throughout Israel (and beyond).An ancient Israelite, wanting to tell the story of the wandering of his ethnic and national ancestors, would have naturally looked to the nomadic peoples around him as models. And indeed, throughout the Bible camels are commonly associated with those tribes who lived in the desert: Midianites, Ishmaelites, Amalekites, Kedemites.The biblical authors simply transplanted the nomadic standards of their time into the distant past.There is nothing deceptive about this. They weren’t trying to trick anyone. They imagined, quite reasonably, that the past was, fundamentally, like their present.They had no real alternative. In ancient Israel, in the period when the Bible was written (which ranges, conservatively, from the 10th to the third century BCE), no one had any way of knowing that camels had not always been domesticated pack animals. After all, we didn’t know that for sure until this past week.Without any evidence to the contrary, it is perfectly natural to assume that things have always been the way that they are now. Today we have more information about the past than any other moment in history. In ancient Israel, they had virtually none.And yet we still fall victim to this basic, very human, historical fallacy.It has been suggested that this anachronism in the biblical text is akin to importing semitrailers into the medieval period. But this is a level of ridiculousness too far.I would suggest that it is more similar to describing a medieval Italian as enjoying pasta with tomato sauce. How many people, even today, know that tomatoes only came to Italy from South America in the 16th century?The camels in Genesis may be “wrong,” but they are not a “mistake.” We all imagine the past to the best of our knowledge, the biblical authors included.The lasting lesson of the camel controversy, such as it is, is a simple one: no writing, not even the Bible, is timeless or without context. Views of the past are contingent on both what we know and how we know it.The Bible is a historical record, but it tells us just as much, if not more, about the people who wrote it as it does about the people they wrote about.Since the stories of the Bible remain so central to who we are as a culture, even today (and even for those who dismiss it), it seems entirely fitting that we should be equally interested in the ancient people who composed them.Despite their lack of historical knowledge — and, equally, because of it — they, more than the characters in the Bible, are our true cultural ancestors.(CNN)ANN.Az



































 Photo
Photo 



 Video
Video